In today’s dynamic business environment, effective project management is crucial for the success of any organization. The project life cycle provides a structured approach to managing projects from inception to completion, ensuring that objectives are met within scope, time, and budget constraints.
Project Life Cycle
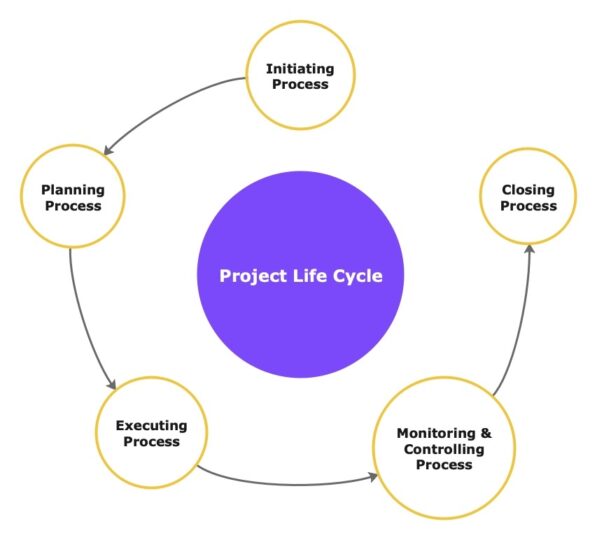
The project life cycle encompasses all the phases a project goes through from initiation to closure. It provides a roadmap for project managers, guiding them through the various stages of project execution.
Phases of the Project Life Cycle
Initiation
The initiation phase marks the beginning of a project. During this phase, the project’s feasibility is assessed, and objectives are defined. Key stakeholders are identified, and the project charter is created.
Are you curious about the flourishing landscape of software development in Costa Rica?
Planning
The planning phase involves developing a detailed project plan. This includes defining project scope, creating a work breakdown structure, estimating resources, and developing a project schedule.
Execution
The execution phase is where the project plan is put into action. Tasks are assigned to team members, and project activities are executed according to the plan. Effective communication and coordination are essential during this phase.
Monitoring and Controlling
The monitoring and controlling phase involves tracking project progress and performance. Key performance indicators are monitored to ensure that the project stays on track. Any deviations from the plan are identified and addressed promptly.
Closure
The closure phase marks the end of the project. Final deliverables are handed over to the client, and project resources are released. A post-project review is conducted to evaluate the project’s success and identify lessons learned.
Key Activities in Each Phase
Each phase of the project life cycle involves specific activities that contribute to the overall success of the project.
Initiation Phase
- Conducting a feasibility study
- Defining project objectives
- Identifying key stakeholders
Planning Phase
- Developing a project plan
- Creating a work breakdown structure
- Estimating resources and budget
Execution Phase
- Assigning tasks to team members
- Monitoring project progress
- Managing project risks
Monitoring and Controlling Phase
- Tracking project performance
- Managing changes to the project scope
- Ensuring quality control
Closure Phase
- Handing over deliverables to the client
- Releasing project resources
- Conducting a post-project review
Project Life Cycle Models
There are several project life cycle models that organizations can use, depending on the nature of the project and its requirements.
Waterfall Model
The waterfall model follows a linear and sequential approach to project management. It consists of distinct phases, with each phase being completed before moving on to the next.
Agile Model
The agile model is iterative and flexible, allowing for frequent changes and adaptations throughout the project life cycle. It emphasizes collaboration and customer feedback.
Spiral Model
The spiral model combines elements of both the waterfall and agile approaches. It involves repeated cycles of prototyping, testing, and refinement, allowing for continuous improvement.
Challenges in Project Life Cycle
Despite its benefits, the project life cycle is not without its challenges. Common challenges include scope creep, resource constraints, and communication issues.
Scope Creep
Scope creep refers to the tendency for project scope to gradually expand beyond its original boundaries. It can lead to increased costs and delays if not managed effectively.
Resource Constraints
Resource constraints, such as limited budget or manpower, can hinder project progress and impact its success. Effective resource management is essential to overcome these challenges.
Communication Issues
Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and conflicts within a project team. Clear and effective communication is critical for project success.
Best Practices for Successful Project Management
To overcome these challenges and ensure successful project management, organizations should adopt best practices such as:
Clear Objectives
Clearly defined project objectives help align team members and stakeholders towards a common goal.
Stakeholder Involvement
Involving stakeholders throughout the project life cycle ensures their needs and expectations are met.
Effective Communication
Regular communication and collaboration among team members promote transparency and accountability.
Tools and Techniques for Project Life Cycle Management
Several tools and techniques are available to help project managers effectively manage the project life cycle.
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts provide a visual representation of project tasks and their dependencies, helping to track progress and identify bottlenecks.
Kanban Boards
Kanban boards enable teams to visualize workflow and prioritize tasks, facilitating efficient task management and resource allocation.
Project Management Software
Project management software such as Microsoft Project or Trello streamlines project planning, execution, and monitoring, enhancing team collaboration and productivity.
Case Studies
Examining real-world examples of successful project implementations can provide valuable insights into effective project management practices.
Successful Project Implementations
Case studies of projects that were completed on time, within budget, and met or exceeded stakeholders’ expectations.
Challenges Faced and Overcome
Examples of projects that encountered challenges such as scope creep or resource constraints but were successfully managed to achieve their objectives.
Future Trends in Project Management
As technology and business environments continue to evolve, the future of project management is likely to be shaped by emerging trends such as:
Automation
The use of automation tools and techniques to streamline project processes and improve efficiency.
Remote Workforce
The increasing prevalence of remote work arrangements, which require new strategies for managing distributed teams and virtual collaboration.
Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into project management tools and processes to enhance decision-making and predictive analytics.
Conclusion
The project life cycle provides a structured framework for managing projects from initiation to closure. By understanding and effectively implementing the project life cycle, organizations can improve project outcomes and achieve their strategic objectives.